UCR’s Center for Economic Forecasting says the region’s housing problem is a land use issue solvable at the local level
Riverside, Ca –“The House That Wasn’t Built. Housing Scarcity: The Inland Empire’s Natural Barrier to Economic Growth” was held Nov. 6 at the Riverside Convention Center. It coincided with the release of a new economic forecast for the U.S., California, and Inland Empire economies.
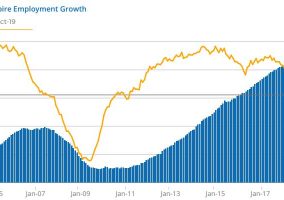
Thornberg said that contrary to the bleak vision of inland California embedded in some statewide economic development agendas, the Inland Empire, which consists of Riverside and San Bernardino counties, has a robust economy and the 14th largest labor force in the nation. Over the past five years the Inland Empire joined the Bay Area in fastest job growth in the state. The region’s unemployment rate of 4% is the lowest it has ever been, equaling that of Los Angeles, and it has the same income per level of educational attainment as Los Angeles and Orange counties.
However, while coastal areas boast large, highly paid professional and technical sectors, healthcare, government, and logistics dominate the Inland Empire’s economy. These jobs often require less education and fewer skills, and generally pay less than jobs in technology, finance, and educated professions that lead the coast.
Rather than regard this as an impediment to developing the kind of economy found in coastal California, Thornberg suggested the Inland Empire’s labor force and housing supply have been necessary supports to California’s growth all along and comparison to coastal areas is both methodologically unsound and unfair.
“Comparing local economies to San Jose is like comparing your health to an Olympic athlete,” Thornberg said. “The only place that looks like San Jose is San Jose.”
The housing supply, however, has not kept pace with the population, which over the past 25 years has grown three times faster than that of the coast. Apartment vacancies, for example, are at less than 4%. The region is not building enough housing, and neither are Los Angeles and Orange counties. This situation will increase regional competition for housing that is already pushing out the Inland Empire’s workforce as housing grows scarcer and rents rise. While some worry the rich are leaving California in droves, far more people at the other end of the spectrum are abandoning the state for places like Nevada and Arizona, where housing is available and affordable.
The Center for Economic Forecasting’s analysis indicates a crisis of housing supply, not affordability. California has the second lowest vacancy rate in the nation and the highest percentage of adults living with parents. Thornberg said California needs to be issuing 200,000-250,000 building permits per year to sustain a 2% job growth rate but is only doing 130,000.
“Lower-skilled workers moved inland because coastal areas put the kibosh on housing 20 years ago,” Thornberg said. “It’s like we’re saying, ‘We already kicked you out of the coastal areas; now we want to kick you out of the inland, too.’”
The center’s analysis finds the housing problem is a land use issue that needs to be solved at the local level. Thornberg said a poorly thought-out tax model exacerbates the housing crisis. Most city revenue comes from business taxes, which encourages local governments to invest in business development, not housing. If cities have to build housing, they want it to be high-end and often enact restrictive laws to prevent high-density alternatives that attract lower-income occupants, like apartment complexes.
“The decisions that need to be made to continue amazing growth in the Inland Empire are local,” said Thornberg. “We need to start having these land use conversations and making decisions.”
About UC Riverside
The University of California, Riverside (www.ucr.edu) is a doctoral research university, a living laboratory for groundbreaking exploration of issues critical to Inland Southern California, the state and communities around the world. Reflecting California’s diverse culture, UCR’s enrollment is more than 24,000 students. The campus opened a medical school in 2013 and has reached the heart of the Coachella Valley by way of the UCR Palm Desert Center. The campus has an annual statewide economic impact of almost $2 billion. To learn more, email news@ucr.edu.